Kali Linux is a Debian-based, open-source Linux distribution specifically designed for information security tasks, including Penetration Testing, Security Research, Computer Forensics, and Reverse Engineering.
This multi-platform nature of Kali Linux provides a robust, stable, and well-known baseline for operation, whether on desktops, servers, virtual machines, live environments, cloud, or containers.
What makes Kali Linux popular among hackers?
Kali’s popularity in the security community stems from its design, which includes tools specifically targeted at penetration testing, security research, computer forensics, and reverse engineering. The TV series Mr. Robot also contributed to its mainstream popularity.
How many tools are included in Kali Linux?
Kali Linux comes pre-installed with over 600 penetration-testing tools, including nmap (port scanner), Wireshark (packet analyzer), John the Ripper (password cracker), Aircrack-ng (for penetration-testing wireless LANs), Burp Suite, and OWASP ZAP (both web application security scanners).
What is the security level of Kali Linux?
Kali Linux is developed in a secure environment with a limited number of trusted contributors allowed to commit packages, each of which is signed by the developer. It has a custom-built kernel that has been patched for injection, as the development team frequently conducts wireless assessments.
Is Kali Linux portable?
Kali Linux can be installed natively on a PC, booted from a live CD or USB, or run within a virtual machine. It supports the Metasploit Framework of the Metasploit Project, a tool for developing and executing security exploits.
Which Linux distribution does Kali Linux derive from?
Kali Linux is based on Debian Wheezy, with most of its packages sourced from the Debian repositories.
Which version of Kali Linux should I download?
Each Kali Linux version is tailored to specific uses or platforms. First, determine your system architecture. The 64-bit ISO is suitable for permanent installations on 64-bit systems. For users wishing to try Kali Linux without installation, portable versions are recommended.
Kali Linux was created by Mati Aharoni and Devon Kearns of Offensive Security, reworking their previous forensics Linux distribution, BackTrack, which was based on Ubuntu. Raphaël Hertzog, the third core developer, joined as a Debian expert.
What’s New
We are pleased to announce the launch of Kali Linux 2025.1a, kicking off the year with enhancements and improvements that streamline user experience. It is now available for download or for upgrading if you’re already running Kali Linux. As for the name, Kali Linux 2025.1a was necessary due to a last-minute bug discovered in a package after our images were produced, necessitating a re-build with a fix.
Here’s a summary of changes since our previous release, December 2024.4:
- 2025 Theme Refresh – Our annual theme update
- Desktop Environment Updates – KDE Plasma 6.2 & Xfce 4.20
- Raspberry Pi – Major kernel updates
- Kali NetHunter CAN – Car hacking capabilities in your pocket
- Packages – A variety of new packages added & numerous updates
2025 Theme Refresh
Continuing our tradition, the first release of the year, 20XX.1, features our annual theme refresh aimed at keeping our interface modern. This year, we are thrilled to introduce a thoughtfully designed theme that enhances user experience from startup. Expect significant updates to the boot menu, login screen, and an impressive selection of desktop wallpapers for both Kali and Kali Purple editions, ensuring that our platform’s aesthetics match its cybersecurity capabilities.
Desktop Environments
KDE Plasma 6.2
We’re excited to unveil the availability of Plasma 6.2 in Kali, marking a significant update from Plasma 5.27. The scope of the changes is extensive, so for detailed insights, check the official announcements: 6.0, 6.1, and 6.2.
All themes have been updated to match the new environment, which includes refreshed window and desktop visuals. Among the most exciting additions? Floating panels!
Xfce 4.20
Our default desktop environment, Xfce, has experienced a minor software update from version 4.18 to 4.20, following two years of development and its formal release on December 15, 2024. This version follows the Xfce 4.18 release that debuted during Christmas of 2022 (Kali 2023.1).
New keyboard shortcuts:
To enhance navigation for users transitioning from other operating systems, we have introduced several keyboard shortcuts for effortless desktop navigation:
- Ctrl + Alt + F: File Manager
- Super + E: File Manager
- Super + F: File Manager
- Super + R: Run Command (in addition to the former Alt + F2)
- Super + T: Open Terminal (in addition to the former Ctrl + Alt + T)
- Super + W: Open Browser
- Super + F1: Locate Cursor
- Super + D: Show Desktop (in addition to the previous Ctrl + Alt + D)
Window Manager shortcuts:
- Super + Shift + Down: Move window to monitor below
- Super + Shift + Up: Move window to monitor above
- Super + Shift + Left: Move window to monitor on the left
- Super + Shift + Right: Move window to monitor on the right
- Super + KeyPad_1: Tile window down left
- Super + KeyPad_3: Tile window down right
- Super + KeyPad_7: Tile window up left
- Super + KeyPad_9: Tile window up right
Check for other Xfce keyboard shortcuts in the keyboard settings dialog or the XFWM4 keyboard section.
Raspberry Pi
Several changes have been made to Raspberry Pi images in 2025.1a:
- A newer package, raspi-firmware, is now in use, aligned with Raspberry Pi OS.
- A new kernel, based on version 6.6.74, derived from the Raspberry Pi OS kernel, is included in all our images, now supporting the Raspberry Pi 5!
The new kernel packages are:
- linux-image-rpi-2712 – Arm64 kernel for the Raspberry Pi 5/500
- linux-image-rpi-v8 – Arm64 kernel for the Raspberry Pi 02W/2/3/4/400
- linux-image-rpi-v7l – Armhf kernel for the Raspberry Pi 02W/4/400
- linux-image-rpi-v7 – Armhf kernel for the Raspberry Pi 2/3
- linux-image-rpi-v6 – Armel kernel for the Raspberry Pi 0/0W/1
Corresponding header packages are linux-headers-rpi-2712, linux-headers-rpi-v8, linux-headers-rpi-v7l, linux-headers-rpi-v7, and linux-headers-rpi-v6. These headers will be pre-installed on the Raspberry Pi images we build. Additionally, 64-bit images will include both 2712 and v8, while 32-bit images will incorporate v7l and v7.
The Nexmon kernel module has been enabled for DKMS and is now available as brcmfmac-nexmon-dkms, allowing for separate updates from the kernel. However, the Nexmon firmware is not included in this release, as we are assessing the optimal way to manage firmware updates with minimal impact and will include this in a future update.
A new partition layout has been introduced, closely mirroring Raspberry Pi OS images. The first (vfat) partition is now mounted at /boot/firmware rather than /boot. Thus, any modifications to config.txt must now be made in /boot/firmware/config.txt. Likewise, kernel command line changes should be made in /boot/firmware/cmdline.txt. A /boot/config.txt file will be included as a reference, containing a warning and indicating the correct file path.
The config.txt file has been simplified, as the newer boot firmware handles several tasks automatically.
Due to many changes under the hood, 2025.1a for Raspberry Pi devices will require starting from a fresh image rather than just following update documentation. While existing setups on the 5.15 kernel will not be affected by updates, we highly recommend starting fresh for the new kernel installation since we do not support upgrades to new kernels.
Kali NetHunter Updates
We are excited to share some fascinating updates for Kali NetHunter in this release. Our team member V0lk3n has added a brand new “CAN Arsenal” tab to the NetHunter app, allowing users to hack cars directly from their pockets! Additionally, he included new kernels for Samsung phones along with a successfully ported Samsung HID patch, which has not worked since the Galaxy S7.
The installer now features a dynamic wallpaper, created by Robin. This means if a new device with a unique resolution is added, there’s no need to port an existing wallpaper. We’ve also included several bug fixes contributed by yesimxev, Robin, and g0tmi1k.
New Kali NetHunter kernels:
- Samsung Galaxy S9 (Exynos9810 – LineageOS 20/Android 13) – Thanks V0lk3n
- Samsung Galaxy S10 (Exynos9820 – LineageOS 21 & LineageOS 22.1) – Thanks V0lk3n
- Xiaomi Redmi Note 6 Pro (Android 11) – Thanks TheKidBaby
New Tools in Kali
This release primarily focuses on package updates, while also bumping the Kali kernel to 6.12. However, no release would be complete without new additions to the network repositories:
- hoaxshell – A payload generator and handler for Windows reverse shells that exploits the http(s) protocol to establish a beacon-like reverse shell.
Miscellaneous Updates
- Here are a few other updates we’ve made in Kali that don’t require detailed explanations:
- Split the live-config build-script into kali-installer & kali-live.
- We aim to refresh the Kali menu in 2025.2.
Kali Website Updates
- We have added three new pages to kali.org:
- Official Kali Linux Wallpapers – From Kali 2019.4 onwards.
- Legacy Kali Linux Wallpapers – BackTrack to Kali 2019.3.
- Community Kali Linux Wallpapers – Featuring remarkable creations from our users.
For more information (and additional details), visit our documentation.
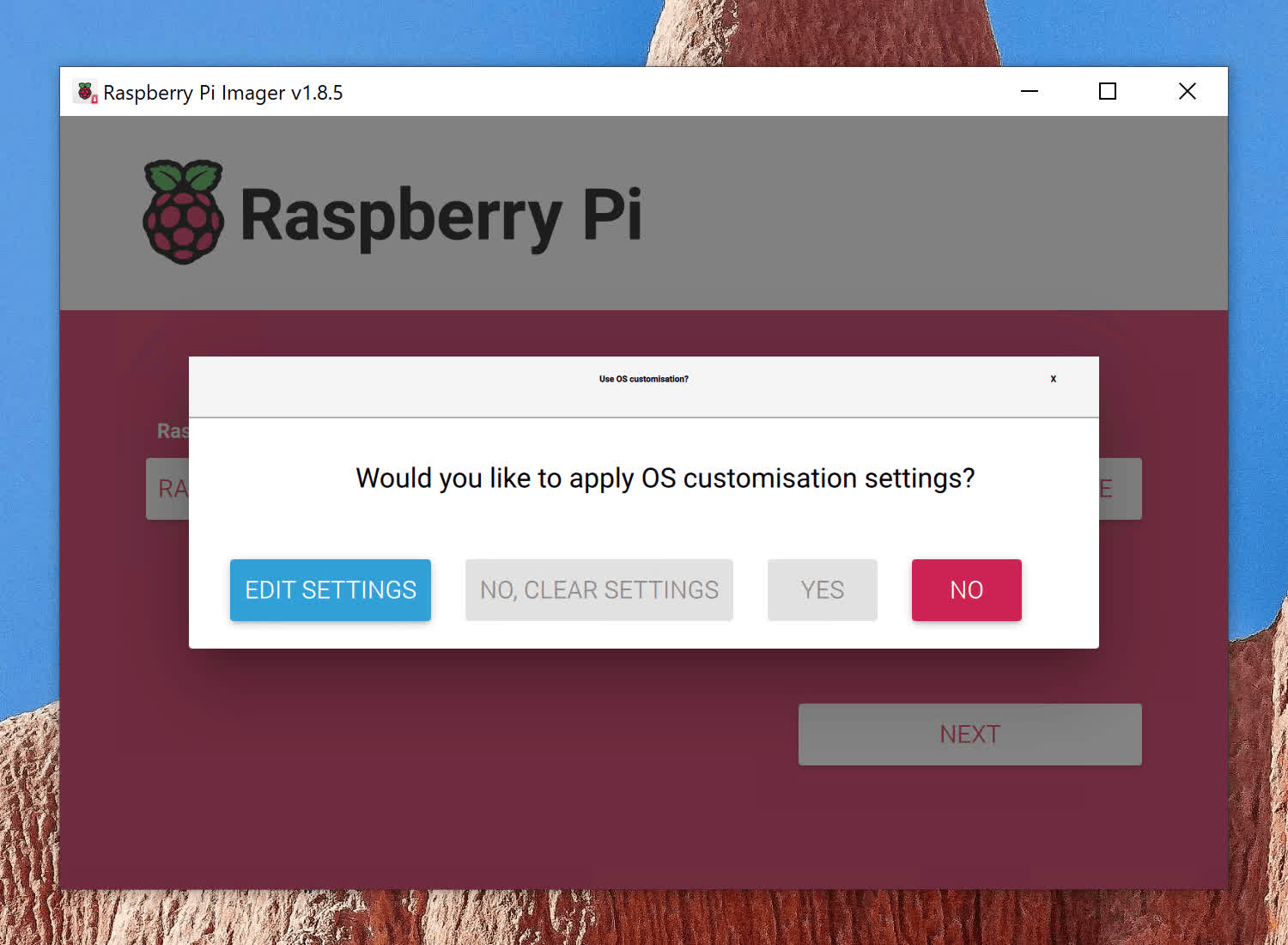
Support for Raspberry Pi Imager Customizations
The wait is over for Pi users! We are thrilled to announce that Kali’s Raspberry Pi images now support applying customizations through the Raspberry Pi Imager software! This exciting update enhances user experience significantly. Whether you’re experienced or new to the platform, this update simplifies your Raspberry Pi experience.
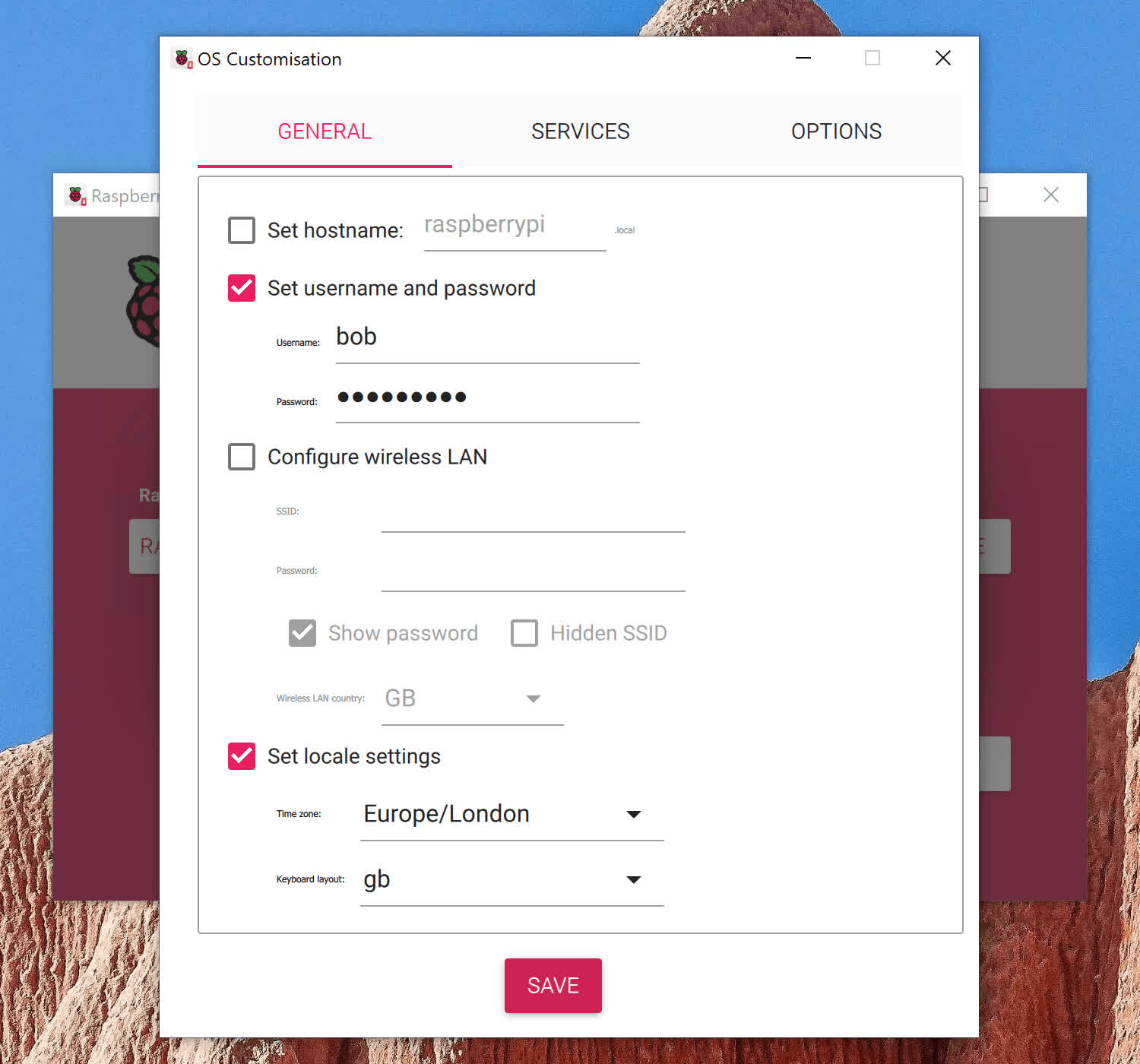
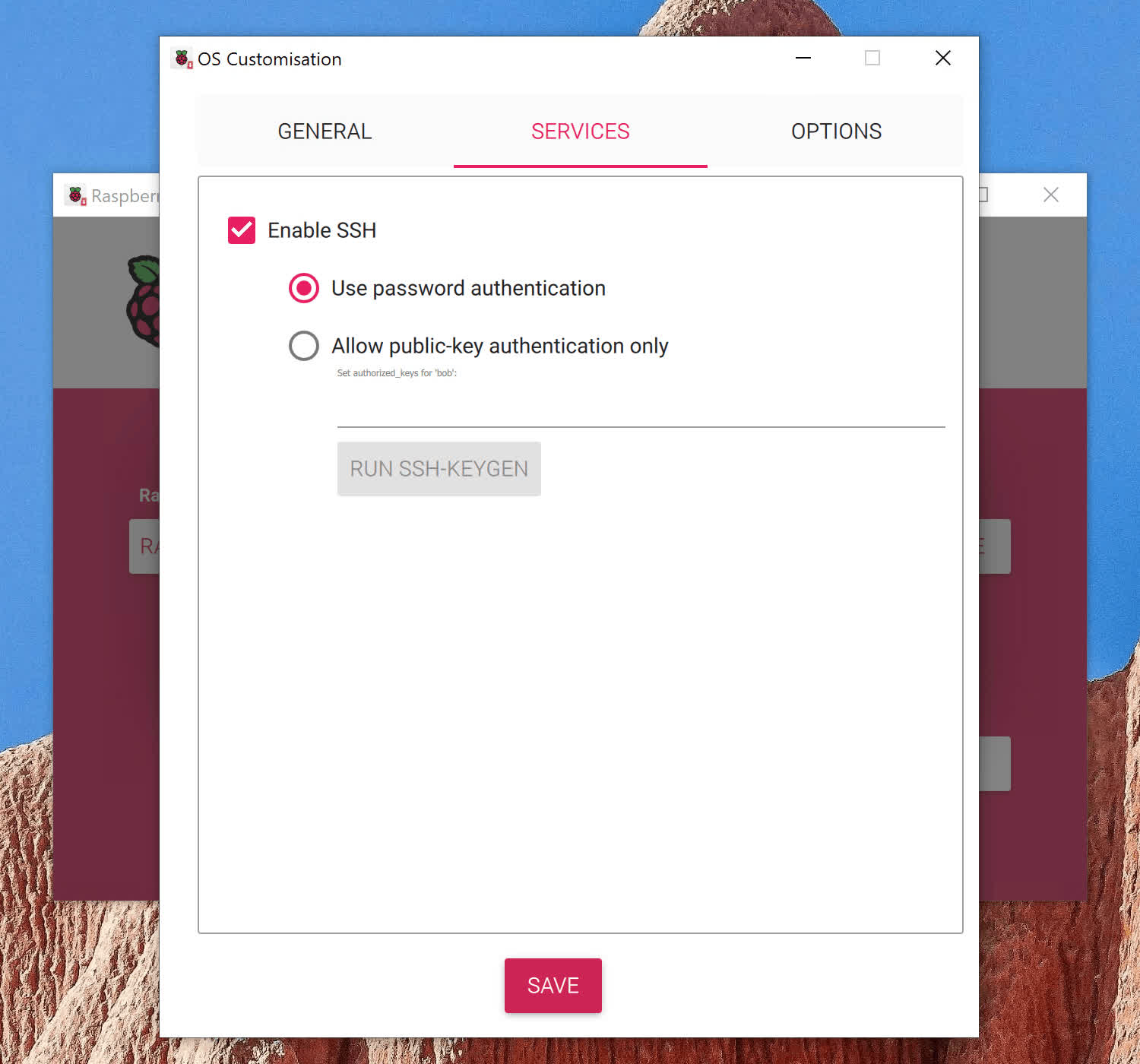
The Raspberry Pi Imager, introduced by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in 2020, is a convenient application that allows users to easily write Raspberry Pi OS images onto SD cards or USB drives. It also enables users to apply necessary customizations before booting their Pi, including setting a custom username and password, choosing a hostname, connecting to Wi-Fi, and even adding an SSH key for remote access.
With this latest release, you can now apply these customizations to all Raspberry Pi images – with the exception of PiTail images, which have unique network and user settings. Unfortunately, due to these customizations, PiTail images do not support customizations through the Raspberry Pi Imager software. For all other images, there are no limitations!
How Does It Work?
The magic occurs when writing a Raspberry Pi image to an SD card or USB drive using the imager software. If customizations are enabled, your settings are stored in two important files on the /boot partition of the drive:
- user-data: This file contains personalized settings, including your username and password, any locale or timezone preferences, and your SSH public key (if you’ve opted to enable SSH).
- network-config: This file contains your Wi-Fi settings along with the pre-computed PSK (Password Security Key) for smooth connectivity.
Upon first boot, the Raspberry Pi applies these custom settings automatically.
Quick tip: Don’t forget to delete these files after the first boot to enhance security.
Default Settings for Non-Customized Images
For users opting out of customizations, rest assured that the default settings for Raspberry Pi images remain unchanged, with “kali/kali” as the username and password.
GNOME 47
We are excited to announce the arrival of the latest GNOME Desktop update, GNOME 47! This update brings countless changes and desktop enhancements, with the standout feature being support for accent color customization. Users can now personally choose their favorite colors for window and shell elements, allowing enhanced control over desktop aesthetics.
From Kali’s perspective, we’ve synchronized this new setting with icon themes and legacy GTK window themes to create a cohesive visual experience across the board. We have also developed multiple theme variants to match various accent colors, which are accessible in other desktop environments as well, enabling you to personalize your Kali experience.
Additional Improvements
Fresh login theme:
Enhanced system-monitor panel extension.
Improved color schemes for gnome-text-editor.
Kali Forums Refresh
A few weeks ago, we launched a refresh of our Kali Forums, now powered by Discourse alongside a new set of moderators selected from our community moderators on Discord. We are pleased with the activity and engagement we are observing on it so far, and we hope to see you there!
For more details, check our blog post about the refresh.
New Tools in Kali
This release introduces 14 new tools to the network repositories! Here’s a concise summary of new additions:
- bloodyad – Framework for Active Directory privilege escalation (Submitted by @Arszilla)
- certi – Request certificates from ADCS and discover templates (Submitted by @Arszilla)
- chainsaw – Rapid search tool for Windows forensic artifacts (Submitted by @Arszilla)
- findomain – Comprehensive solution for domain recognition (Submitted by @Arszilla)
- hexwalk – Hex analyzer, editor, and viewer.
- linkedin2username – Generate username lists for companies on LinkedIn.
- mssqlpwner – Interact and penetrate MSSQL servers.
- openssh-ssh1 – SSH client for legacy SSH1 protocol.
- proximoth – Tool for detecting control frame attack vulnerabilities (Submitted by @TechnicalUserX)
- python-pipx – Execute binaries from Python packages in isolated environments.
- sara – RouterOS Security Inspector (Submitted by @casterbyte).
- web-cache-vulnerability-scanner – Go-based CLI tool for testing web cache poisoning (Submitted by @Arszilla).
- xsrfprobe – Advanced toolkit for auditing and exploiting Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF/XSRF).
- zenmap – Network Mapper (nmap) front-end, eliminating the need for zenmap-kbx.
There have been numerous package updates and added libraries. Additionally, we have upgraded the Kali kernel to 6.11!
Kali Linux 2024.3 Release (Multiple Transitions)
As summer wraps up, it marks the end of package migrations, allowing Kali 2024.3’s release. You can now begin downloading or upgrade if you have an existing installation.
The changelog summary since the June 2024.2 release is:
Qualcomm NetHunter Pro Devices – Qualcomm Snapdragon SDM845 SoC is now supported.
New Tools – 11 new tools have been added to your arsenal
Our focus has predominantly been on behind-the-scenes updates and optimizations since the last release. There have been extensive migrations concerning multiple stacks. Following the completion of the t64 transition, we proceeded directly into several additional transitions like GCC 14, glibc 2.40, and Python 3.12.
This last change is critical because Python 3.12 has removed some long-deprecated APIs, resulting in some package breakages. We have worked diligently to address these issues, and while we are close to completion, Python 3.12 will become the default in the next Kali version – 2024.4. A significant change for users will be that installing Python packages using pip will no longer be possible. We sought to inform users of this over a year ago and encourage those heavily reliant on pip to review the implications.
However, for now, this release, 2024.3, maintains Python 3.11 as the default interpreter.
Consequently, as the new Python 3.12 stack has not yet gone live in Kali-rolling, it has inadvertently blocked other seemingly unrelated packages from entering the distribution. Therefore, the past two months have seen a slowdown in updates within Kali-rolling, resulting in this release being less exhilarating than usual. This temporary decrease will cease shortly as Python 3.12 hits Kali-rolling, at which point package updates will resume their usual pace. Users of Kali-rolling should anticipate a surge of updates!
Eventually, despite packaging, progress has been made on various projects that are not ready for release just yet, including a new Kali forum, updates for the NetHunter Store, and refreshing the Kali menu.
New Tools in Kali
This Kali release emphasizes package updates. For end-users, it primarily revolves around the new tools added; for us, it’s about the updated stacks!
Our community, once again, has contributed with fresh tools. Long-term contributor @Arszilla has been particularly active! Here’s a highlight of the new tools added to the network repositories:
- goshs – A Go-based SimpleHTTPServer with added features.
- graudit – A source code auditing tool that employs grep.
- gsocket – Facilitate communication between two machines across different networks.
- hekatomb – Extract and decrypt credentials from all domain computers (Submitted by @Arszilla).
- mxcheck – Info and security scanner for email servers (Submitted by @Arszilla).
- netexec – A network service exploitation tool designed to automate security assessments for expansive networks (Submitted by @Arszilla).
- netscanner – A modern TUI network scanner & diagnostic tool (Submitted by @Arszilla).
- obsidian – A private and adaptable writing application catering to various thought processes.
- sippts – A suite of tools for auditing SIP-based VoIP systems (Submitted by @Arszilla).
- sprayhound – A password spraying tool with Bloodhound integration (Submitted by @Arszilla).
- sqlmc – A tool for checking all URLs on a domain for SQL injections (Submitted by @Arszilla).
Access continues for numerous package updates and newly added libraries as well. We also successfully upgraded the Kali kernel to 6.8.
Kali NetHunter Updates
Kali NetHunter 2024.3 has been temporarily halted while we enhance the build infrastructure. We will release the updated images once ready (anticipated in a few weeks) and discuss new features in the next Kali release, 2024.4 (goodbye Mana!).
On a brighter note, we are pleased to announce support for new devices! We are excited to provide Kali NetHunter Pro images for devices equipped with Qualcomm Snapdragon SDM845 SoC (System on Chip), including:
- OnePlus 6/6T
- SHIFT SHIFT6mq
- Xiaomi Pocophone F1 (also known as Poco F1)
Thanks to @Shubhamvis98 for his incredible work in bringing this to fruition!
Moreover, exciting news for Hungarian NetHunters! Check out the “HnLVIP NetHunter” podcast (aired August 1, 2024) by @hackeslangos featuring @yesimxev, discussing NetHunter, an OffSec journey, and much more! You can listen to it here.
Kali ARM SBC Updates
- QEMU_CPU=cortex-a72 has been added to the build scripts when creating an arm64 image on an amd64 host, significantly accelerating the process.
- USBArmory devices should now correctly initiate their DHCP server.
- Support for the Raspberry Pi 4 Compute Module Wi-Fi device has been integrated.
- The kernel version for the Raspberry Pi 5 has been upgraded to 6.6.
- Due to the updated firmware, users using A2-rated microSD cards can expect a 2-3x speed increase in random access.
- The Pinebook kernel has reverted to a 6.1 version to address graphical issues and LCD malfunctions found in newer kernels.
- We have streamlined the build dependencies list, minimizing unnecessary installations for users compiling their own custom images.